
Ivan Pavlov: biography
Ivan Pavlov is a famous Russian scientist whose works are highly appreciated and recognized by the scientific community. The scientist made important discoveries in physiology and psychology. Pavlov is the founder of the study of the higher nervous activity of men.
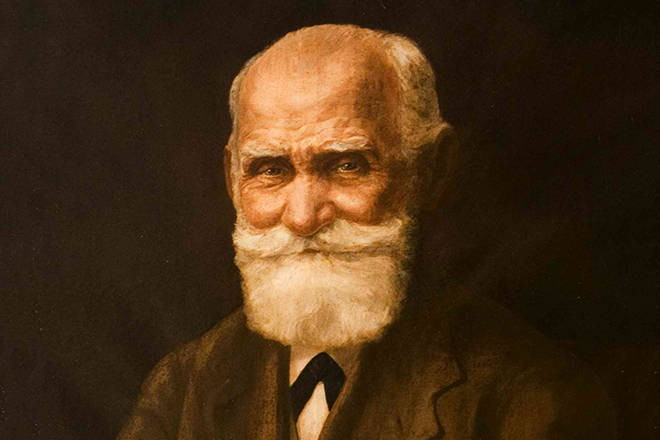
Ivan Petrovich was born on September 26, 1849, in Ryazan. He was the first child out of ten in the Pavlov family. Mother Varvara Ivanovna (nee Uspenskaya) was brought up in the family of priests. She was a strong, cheerful girl before marriage. Childbirth adversely affected the health of the woman because it followed one another. She was not educated, but she was intelligent, down to earth and diligent from birth.
The young mother brought up the children in a right manner. She instilled qualities, which helped the children to realize their potential in the future successfully. Peter Dmitrievich, Ivan's father, was a truthful and independent priest of peasant origin. He ministered in a poor parish. He often came into conflict with the church staff; loved life, never got ill, willingly worked in the garden and vegetable garden.

Over time, Peter Dmitrievich became a rector of the temple in Ryazan due to his goodness and pastoral zeal. The father was an example of persistence in achieving goals and striving for excellence. Ivan respected his father and listened to his opinion. In 1860, the boy entered the church school on the insistence of his parents and studied the initial course of the theological seminary.
In his early childhood Ivan rarely got ill, he grew up as a cheerful and strong boy, played with children and helped his parents in the household. The father and mother have instilled in children the habit of working, taught them to maintain order in the house and to be careful. The parents worked hard and they demanded the same from children. Ivan with younger brothers and sisters hauled water, split wood, stoked the fire and did other household duties.
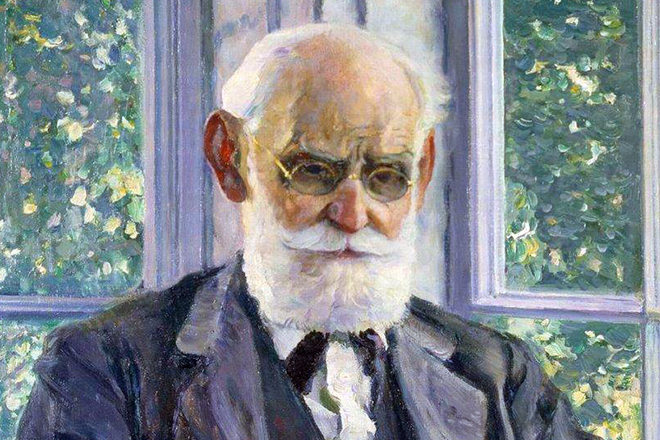
The boy started his education at the age of eight, but he went to school at 11. The reason for this was a severe bruise, which he got falling down the stairs. The boy lost his appetite, sleep, he began to grow thin and turn pale. Home treatment did not help. He began to recover, when the child, worn out by disease, was taken to the Trinity Monastery. His guardian was the hegumen of the divine abode, who once stayed at the Pavlovs' house.
He managed to recover health and vitality, thanks to gymnastic exercises, good food, and fresh air. Hegumen was educated, well-read and led an ascetic life. Ivan learned and knew the book, donated by the guardian, by heart. It was the collection of Krylov’s fables, which later became his handbook.
Seminary
Ivan decided to enter the seminary in 1864 under the influence of the spiritual mentor and parents. He studied natural sciences and other interesting subjects, participated actively in the discussions. Throughout his life, he was an ardent polemicist. He fiercely fought with the enemy, countering any arguments of the opponent. Ivan was the best student in the seminary, and he was additionally engaged in tutoring.
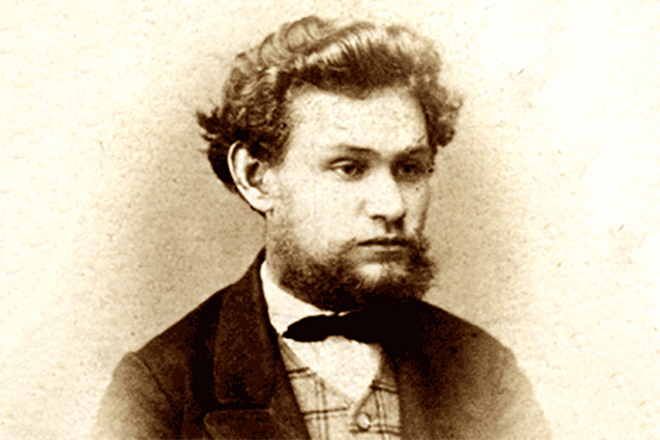

He got acquainted with the works of the great Russian thinkers. The student was imbued with their desire to fight for freedom and a better life. Over time, he focused on natural science. The monograph of I.M. Sechenov “Reflexes of the Brain” played an important role in it. He realized that the career of a churchman was not interesting to him. Ivan began to study the subjects that were necessary for entering the university.
Physiology
In 1870 Pavlov moved to Petersburg. He entered the University and studied well. At first, he did not get a scholarship, as he had to change one department to another. Later, a successful student was awarded an imperial scholarship. Physiology was his main passion, and in three years it became his main priority. Under the influence of the scientist and experimentalist I. F. Tsion, the young man finally chose and devoted himself to science.
In 1873, Pavlov began to explore the lungs of frogs. He wrote a scientific work on how the laryngeal nerves affect the blood flow together with one of the students and under the supervision of I. F. Tsion. Later, he studied the pancreas together with the student M. M. Afanasyev. The research work was awarded a gold medal.

Pavlov graduated a year later, in 1875, since he had to repeat a year. His research took a lot of time and energy, thus, he failed the final exams. Upon graduation, Ivan was only 26 years old. He was very ambitious and expected a great success.
Since 1876, Pavlov got a position as an assistant to Professor K. N. Ustimovich in the Medical Military Academy and at the same time, he studied the physiology of blood flow. The works of this period were highly appreciated by S.P. Botkin. The professor invited the young researcher to work in his laboratory. There Pavlov studied the physiological characteristics of blood and digestion.

Ivan Petrovich worked in S. P. Botkin’s laboratory for 12 years. The scientist’s biography of this period included events and discoveries that brought him world fame. It was the period of change.
It was not easy for a simple man to achieve this in pre-revolutionary Russia. The fate gave him a chance after a number of unsuccessful attempts. In the spring of 1890, he was offered the position of chairman at the Warsaw and Tomsk Universities. In 1891 the scientist was invited to the Institute of Experimental Medicine to organize and create the Department of Physiology.
Pavlov supervised this department until the end of his life. He conducted research on the physiology of digestive glands at the University. In 1904 he won the Nobel Prize, thus, becoming the first Russian Nobel laureate in Medicine.
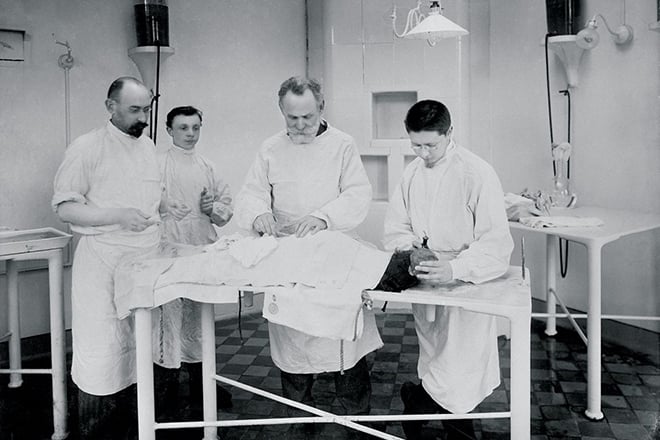
The Bolshevik revolution had a positive impact on the scientist. V.I. Lenin appreciated his works. The academician and all employees had favorable opportunities for fruitful work. The laboratory was changed into the Institute of Physiology during the Soviet regime. They opened a college town near Leningrad by the 80th anniversary of the scientist, he published the studies in the best publishing houses.
They opened clinics at the institutes, purchased modern equipment, and increased the staff. Pavlov received funds from the budget and extra money for expenditure, felt gratitude for such an attitude to science and himself.
Pavlov's Dog
The feature of Pavlov's method is the ability to see the connection between physiology and mental processes. Work on the mechanisms of digestion became the starting point for the development of a new direction in science. Pavlov studied physiology for more than 35 years. He created the concept of conditioned reflex.
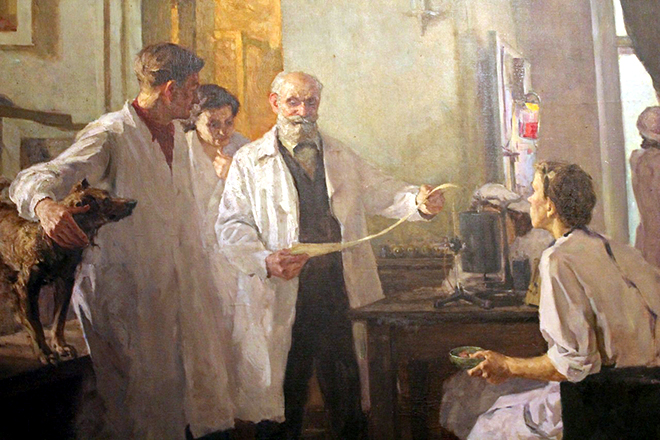

The experiment, called "Pavlov's dog," consisted in studying the reflexes of an animal in response to an external stimulus. In the course of it, he gave the dog food after a signal of a metronome. After a few repetitions, the dog started to salivate in response to the stimulus without food. The scientist deduced the concepts of the reflex, which is formed on the basis of experience.
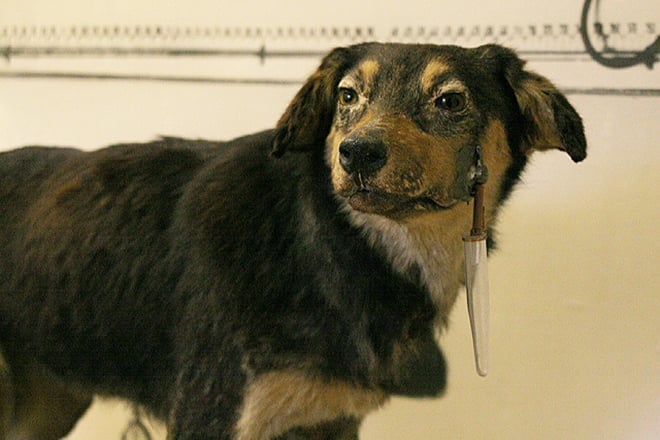

In 1923, the first study of the twenty-year experience to animals was published. Pavlov made the most serious contribution to the studying of brain functions in science. The Soviet government supported the studies which were very significant.
Personal life
The talented young man met his first beloved woman, the future teacher Seraphima Karchevskaya, in the late 1870’s. Young people share common interests and ideals. They married in 1881. Two daughters and four sons were born in the family.
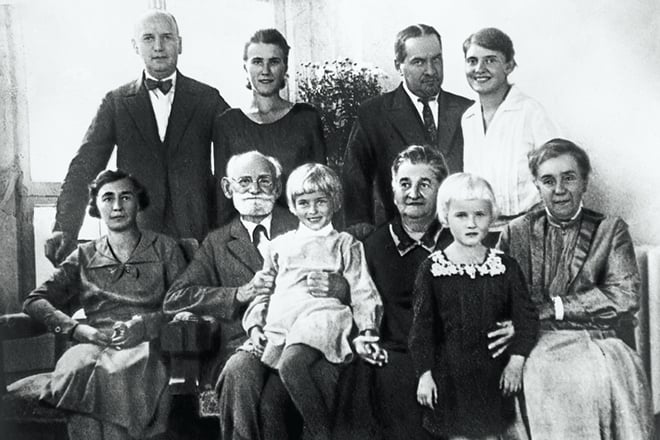

The first years of family life were difficult because they had no their own house, there was not enough money for living. The tragic events connected with the death of the first child and another young child damaged the health of his wife. It threw Ivan off his stride and made him desperate. Seraphima encouraged and comforted her husband, and helped the man to overcome the gravest melancholy.
Later, the couple's personal life improved and it did not hamper the young scientist to develop a career. The constant support of his wife also contributed to it. Ivan Petrovich was respected among scientists, and people liked him because of his cordiality and enthusiasm.
Death
There is a cheerful, handsome, bearded man in the photo taken during the life of a scientist. Ivan Petrovich had a strong health. The exception was cold that sometimes had complications in the form of pneumonia.
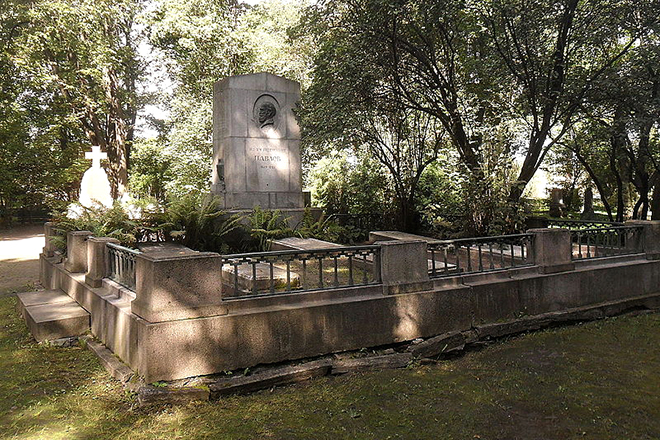
Pneumonia caused the death of the 87-year-old scientist. Pavlov died on February 27, 1936, his grave is at the Volkovo Cemetery.
Works
- The Centrifugal Nerves of the Heart. Doctor's thesis;
- Twenty-five Years of Objective Study of the Higher Nervous Activity of Animals;
- Lectures on the Work of the Cerebral Hemisphere.;
- Physiology and Pathology of Higher Nervous Activity;
- Reports on the Physiology and Pathology of Higher Nervous Activity;
- Collection of Works;
- Theory on the Physiology of Blood Circulation;
- Theory on the Physiology of the Nervous System.





