
Helmut Kohl: biography
Helmut Kohl is a German politician who served as Chancellor of the country three times. Kohl influenced the process of reunification of the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, Germany's accession to NATO and establishment of the euro currency instead of the Deutsche Mark.
Helmut Kohl was born on April 3, 1930, in the family of a financier. Helmut’s hometown is Ludwigshafen. Father Hans was born in Bavaria. The boy's mother was Cäcilie. Besides Helmut, the family brought up two more children.
Kohl’s family always paid attention to politics. The father and mother were conservative but Roman Catholics. During the Second World War, Helmut's elder brother died. The future politician was to defend the country during the war. But he was not involved in any combat.
In 1950, the guy decided to develop his career, and he became a student at University of Frankfurt. The young man liked to study law. But a year later Kohl left the University and switched to Heidelberg University, where Helmut studied history and political science.
Politics
Helmut Kohl’s politician career began in his school years when the boy joined the Christian Democratic Union. Later, Kohl created the Youth Union in Ludwigshafen. He was involved in politics more and more every year, so in 1953 Helmut joined the board of the CDU. Later, the young man became deputy chairman of the Junge Union-branch in Rhineland-Palatinate.

The career of the politician developed gradually. By 1968 Helmut Kohl already had senior positions in the Christian-Democratic Union. As a result, they elected the young man vice-chair of the party. Fritz Ries helped a lot the development of Kohl’s politician career.
In addition to the post of party chairman, Helmut became Minister President in Rhineland-Palatinate. The man initiated an administrative reform, later founded the University of Trier-Kaiserslautern, which is now known as Trier University and The University of Kaiserslautern.

Three years later, the party had the elections. Kohl lost, and Rainer Barzel became the chairman of the CDU. But the rival's joy was short-lived. In 1973, Helmut was invited to this position again. The politician remained chairman until 1998.
In 1976, Kohl had a desire to move on. It was the time of the Bundestag elections. The politician decided to try his fate and to run for Chancellor. The promotion was successful. Kohl’s party received 48.6% of the vote. It was a small victory for the party members as the CDU and Helmut could not win the state elections.
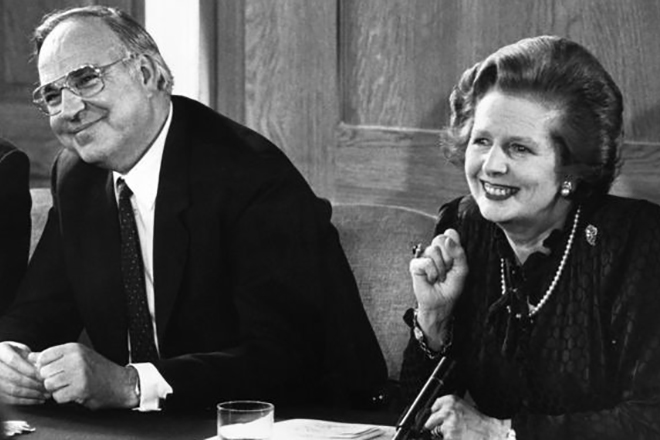

Thus, Kohl retired as minister-president to become the leader of the CDU/CSU in the Bundestag. But unexpectedly representatives of the Christian-Social Union decided to withdraw from the united faction. Helmut could not allow this. So he had to use different methods to resolve the issue and to preserve the unity of the party members. From 1976 to 2002 Kohl was in the Bundestag as a deputy.
Helmut Kohl officially took the post of Federal Chancellor of Germany on October 1, 1982. The politician replaced Helmut Schmidt after the CDU proposed a constructive vote of no confidence. Such a decision led to problems within the Free Democratic Party, as Kohl was not elected Chancellor by ordinary voting.
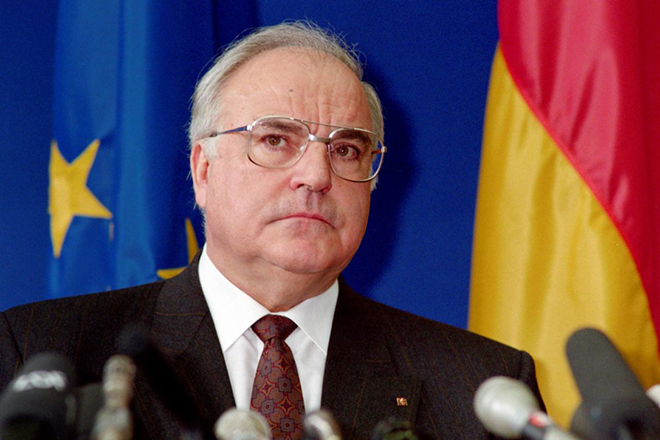

But Helmut wanted to achieve mutual understanding. He asked the members of the Bundestag one single question whether they trust Kohl as Chancellor or not. Many deputies decided to stay on the sidelines, so Kohl got what he wanted. A year after Helmut had been appointed Chancellor, the FRG President addressed the deputies. The politician announced the dissolution of the Bundestag.
France and Germany had tense relations for a long time. But in 1984 everything changed. Longtime opponents Helmut Kohl and Francois Mitterrand met on the battlefield at Verdun. The photo with their handshake spread around the world and became a reliable proof of the reconciliation of two countries.
When Helmut Kohl ruled the country, Germany's foreign and domestic policies had both positive and negative results. The politician attracted increased attention after the Flick Affair. Helmut was called into the investigation committee because of the bribery in the government.
In November 1989, the Berlin Wall came down. There were significant changes towards democracy in the GDR. As a result, Kohl presented in the Bundestag a plan that would help bring Germany and the rest of Europe closer. But he did not consult this project with his coalition partners.

In the middle of 1990, the Federal Republic of Germany and the GDR signed an economic and social union treaty. This financial reform negatively affected enterprises. Helmut Kohl could compel the heads of European states to cooperate and coordinate the unification of the FRG and the GDR. Later, Germany joined NATO thanks to the politician.
The union allowed Helmut to develop a political career. Foresight and knowledge of psychology helped the man to prevent the coup in 1989. Its initiators were Heiner Geißler, Lothar Späth, and Rita Sysmut.
In January 1991, Helmut Kohl was re-elected as Federal Chancellor. Minister President of the state of Saarland Oskar Lafontaine became the rival at this election. Since then, the name of Helmut was connected with the unification of Germany, since the politician became the first federal chancellor of the new territories.

Three years later, Kohl was re-elected again. This time the elections were challenging, but Minister-President of Rhineland-Palatinate Rudolf Scharping could not confront Helmut. Since then, Kohl chose a different tactic of the foreign policy. He got Frankfurt am Main as the seat for the European Central Bank. The euro replaced the Deutsch marks.
Kohl did not pay much attention to the internal affairs of the state. It was the reason for the loss of the CDU in the elections to the Bundestag in 1998. It meant resignation for Helmut. In 2002, Kohl refused to run for reelection.
Personal life
The politician's life did not attract public attention. In 1960, Helmut married a young woman, Hannelore Renner. The wife worked as an interpreter. It is known that young people met 12 years before the wedding.
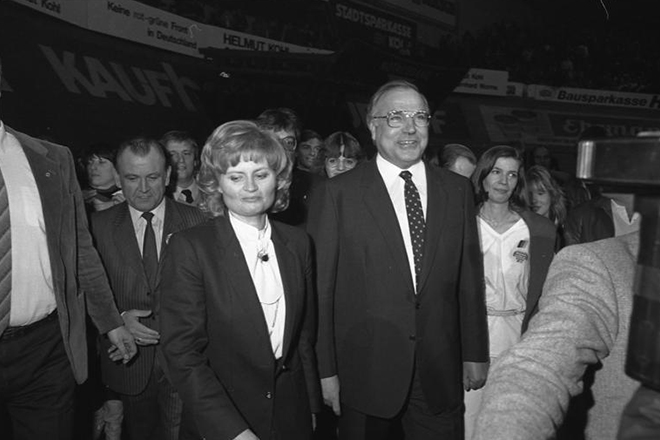

However, they started a love affair later. They had sons in this marriage. Hannelore was allergic to daylight for a long time. Every day deprived the woman of strength, so in July 2001 at the age of 68 years, the spouse of the politician committed suicide.
At the age of 78, Helmut fell in love again. His beloved woman was Maike Richter. The woman worked as an economist. Maike served in the economic department of the German Chancellery.

There is an interesting fact about Richter and Kohl’s wedding. The ceremony was held at the Heidelberg hospital. At that time, the politician was making a recovery after a severe injury, received during the fall. Close relatives and friends of the couple attended the celebration.
Helmut published the first book in 2004. Kohl dedicated this volume, titled "Memories: 1930-1982", to his demised wife, Hannelore. The politician wrote with love about the mother of his children, and he believed that he owed his career to his wife. The second volume appeared on the bookshelves a year later, and the third book was published in 2007.
Death
Helmut Kohl was seriously ill. During the last months of his life, the politician did not appear in public. On June 16, 2017, the man's relatives announced the death of the former German Chancellor. Helmut's close relatives did not declare the official cause of death. But the media reported that the politician died of complications after a gall bladder operation.
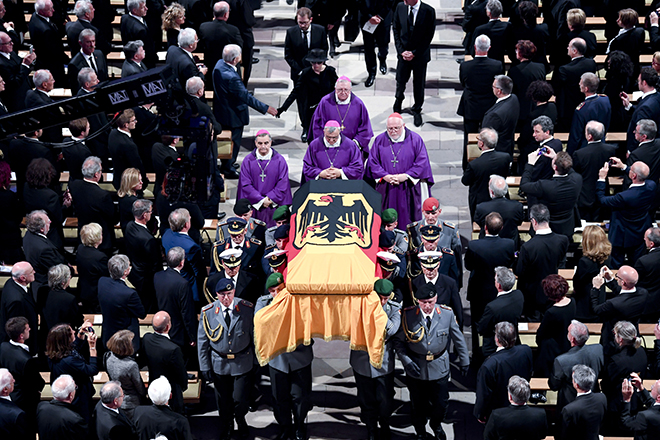

The funeral of Helmut Kohl took place on July 1. The farewell ceremony was held in the European Parliament in Strasbourg. Speakers included former President of the United States Bill Clinton, Chancellor of Germany Angela Merkel, Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev. The grave of the politician is located in Speyer.
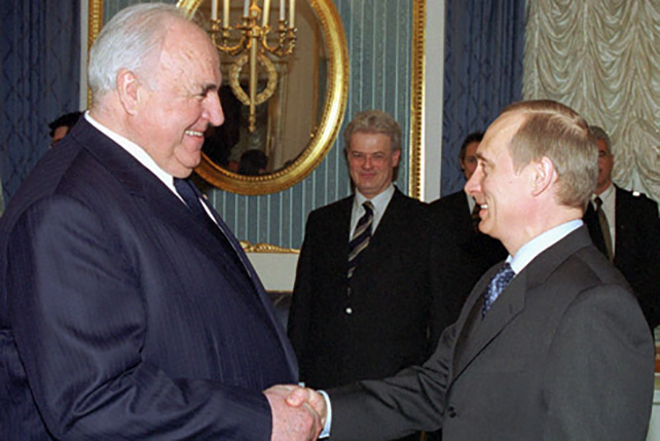
Mikhail Gorbachev was not present at the ceremony. Doctors forbade the ex-president of the USSR to go to Strasbourg because of health problems. The head of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin expressed his condolences and said that Kohl influenced his political views a lot.
Interesting facts
- Helmut Kohl initiated the reunification of Germany.
- The German Chancellor signed the Maastricht Treaty, which established the European Union.
- Helmut Kohl’s political career ended due to a corruption scandal.
- Helmut Kohl wrote several memoir books.
- At the age of 16, he joined the Christian Democratic Union.
Bibliography
- 2004 - "Memories: 1930-1982"
- 2005 - "Memories: 1982-1990"
- 2007 - "Memoirs. 1990-1994."





